CNC Milling and Turning
What is a machine ?
Definition – Machine is a device which can convert one form of energy to another form and simultaneously reduce human effort.
What is a tool ?
Tool is a device which makes our work easier.
Machine Tool – M/C which can produce its own parts (not all) as well as other parts. Ex – Lathe, Milling M/C
M/Cing Centre – In this type of M/C a number of operations can be carried out with the help of automatic tool changer in a single setting of the workpiece.
1. Horizontal Machining center
2. Vertical machining center
M/Cing Process – The process by which requied shape and size is given to the raw material by the help of M/Cing tool
1. Conventional M/Cing process
2. Non Conventional M/Cing process
Difference between conventional an non-conventional M/Cing process?
Conventional M/Cing Process – M/Cing tool directly touches the workpiece. Cutting tool material is harder than the workpiece material.
Ex – CNC Milling, CNC Turning
Non Conventional M/Cing Process – There is a gap between cutting tool and workpiece at the time of machining. Cutting tool may be harder or softer than the workpiece.
Ex – EDM – Electric Discharge Machining
LBM – Laser Beam Machining
AJM – Abrssive Jet Machining
ECM – Electro Chemical Machining

What is Lathe and Milling Machine?
Lathe M/C – Machine tool generally used to produce or manufacture cylindrical or round types of job in which workpiece rotates and cutting tool is fed on the surface of the job to get desired shape and size.
Milling M/C – Machine tool generally used to produce or manufacture flat or irregular type of jobs in which cutting tool rotates and workpiece is fed under the surface of the cutter to get desired shape and size.
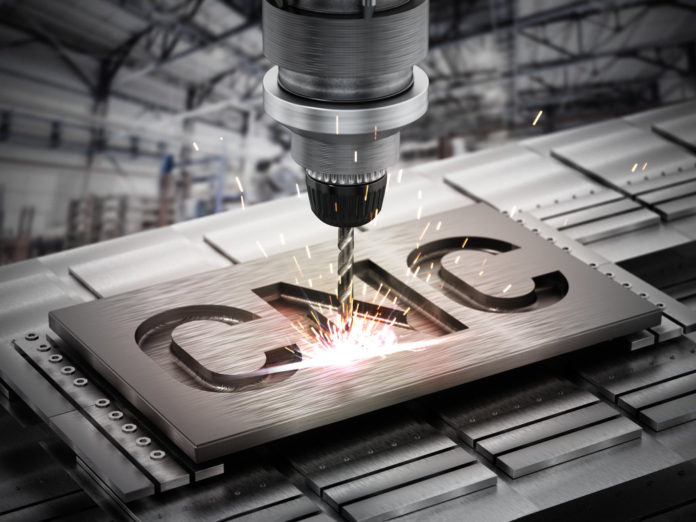
CNC Machine – M/C controlled by certain letters, numbers, and symbols in the form of program by the help of computer.
History of CNC –
1949 – US Air force demanded NC
1952 – Prototype CNC Punched tape input
1980 – CNC Link to controller
1990 – DNC drip feets
Motors used in CNC Machine:
1. Servo Motors – used for X and Z axis movement of the turret, Spindle rotation
2. Induction Motors – used for circulating coolant, lubricating oil, hydraulic oil