Important Financial terms in India
CBS – Core Banking System ; The information related to the customer’s account is stored in the centre server of the bank instead of branch server.
CORE – Centralised Online Realtime Exchange
NEFT – National Electronic Fund Transfer ( Batch Processing )
A nationwide system that facilitates individuals to electronically transfer funds from any bank branch to any individual having an account with any other bank branch in the country.
NEFT transaction takes a maximum of 48 hours to get done. There are no limits upper or lower for NEFT.
Timings of NEFT ;
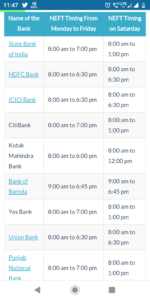
https://www.bankbazaar.com/ifsc/neft-timings.html
RTGS – Realtime Gross Settlement: RTGS System is a fund transfer mechanism for transfer of money from one bank to another on a real time and on gross basis. Real time means payment transaction is not subjected to any waiting period. The transactions are settled as soon as they are processed.
Gross Settlement means transaction is settled on one to one basis without bunching with any other transaction.
Minimum amount for RTGS transaction – ₹ 2 Lac
Maximum limit – ₹ 10 Lac per day.
Follow the link below for RBI’s explanation of RTGS;
https://m.rbi.org.in/Scripts/FAQView.aspx?Id=65
SBI link for detailed explanation on difference between RTGS and NEFT; www.onlinesbi.com/personal/neft_rtgs_faq.html
ECS – Electronic Clearing Service:
ECS is a mode of electronic funds transfer from one bank account to another bank account using the services of clearing house.
Demat account – A demat account is one that allows you to buy, sell as well as transact without the need of any paper work.
Demat means dematerialized account. It means conversion of the hard copy of shares into soft copy.
Rematerialisation means conversion of soft copy of the shares into hard copy.
Financial Inclusion – Financial Inclusion means the delivery of banking services at an affordable cost to the vast section of disadvantaged and low income groups.
BSBDA
No fill Account. Swabhiman
PMJY
BSBDA explanation by RBI;
https://m.rbi.org.in/Scripts/FAQView.aspx?Id=97
PMJY’s official website;
https://www.pmjdy.gov.in/
FDI – Foreign Direct Investment.
FDI is a long term financial investment brought into the country from abroad through subscribing to the stock and debentures of companies in India.
FII – Foreign Institutional Investor
FII are the investor who make investment in the Indian Stock Market such as mutual funds, pension funds securities and assets management companies.
FII make investment for short term purpose. FII need to be registered with the SEBI and approval from RBI is also required.
FDI – Long term Infrastructure
FII. – Short term share
NPA – Non Performing Assets
An asset including leased asset becomes non performing when it ceases to generate income for the Bank.
NBFC – Non Banking Financial Company – A company is treated as NBFC if its financial assets are more than 50% of its total assets. Also the income from the financial assets should be more than 50% of the Gross income. Ex – LIC, Muthoot Finance.
Money Laundering – (washing of money). The process of converting illegal or dirty money through the cycle of transaction so that it turns out as legal or yield money.
Hard Currency – It refers to a currency created in foreign exchange market for which demand is persistantly high relative to supply.
Hot currency – it refers to funds which flows into a country to take advantage of favourable rate of interest in that country. These funds are highly volatile and will be shifted to another foreign exchange market and make when relative interest rate favours the move.
Cheap Money – Money which is available at low rate of interest is known as cheap Money.
Dear Money – The money available at exceptionally high rate of interest is called dear Money.