Material Science/ Metallurgy/ Mechanical Interview Questions
Answers are marked bold
Q.1 ] A Surface hardening process for medium and high carbon steels making use of oxy-acetylene flame
is known as ________
A. Cyaniding
B. Nitriding
C. Flame hardening
D. Induction hardening
Q.2 ] Capacity of a material to store strain energy is known as ______.
A. Resilience
B. Creep
C. Fatigue
D. Stiffness
Q.3 ] Which is not a indentation testing machine?
A. Rockwell Hardness Test
B. Knoop’s Hardness Test
C. Shore’s Scleroscope Hardness Test
D. Monotron Hardness Test
Q.4 ] The ease with which a material can be deformed in to desirable shape while in solid state, with or without heating is called _______
A. Formability
B. castability
C. weldability
D. machinability
Q.5 ] ________ is a solid solution of carbon in γ iron and may possess a max of about 2% carbon at about 1130˚c.
A. martensite
B. austenite
C. pearlite
D. all of these
Q.6 ] Shock absorbing capacity of a material is called _______.
A. Resilience
B. Toughness
C. Stiffness
D. Creep
Q.7 ] A surface hardening process utilizing addition of carbon to the outer layer of mild steel .
A. hardening
B. tempering
C. surface hardening
D. case-hardening (by carburizing)
Q.8 ] A heat-treatment process of improving toughness of already hardened steels is called _______.
A. Hardening
B. Tempering
C. Surface hardening
D. Nitriding
Q.9 ] Failure of material under alternating stresses is known as :
A. stiffness
B. toughness
C. fatigue
D. hardness
Q.10 ] The heat-treatment process which improves softness and ductility in steels and other already cold
worked metals is known as _______.
A. Normalizing
B. Annealing
C. Hardening
D. All of the above
Q.11 ] The ______% of carbon presents in pearlite
A. 0.8%
B. 0.2%
C. 0.5%
D. 0.06%
Q.12 ] Select the correct order of the points A-F in the given figure :
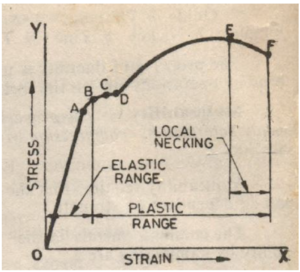
A. breaking stress (stress at fracture or rupture) (fig)
ultimate strength (max load stress)
yield point
elastic limit
proportional limit
B. proportionality limit
elastic limit
yield point
ultimate strength (max load stress)
breaking stress (stress at fracture or rupture)
C. elastic limit
yield point
ultimate strength (max load stress)
breaking stress (stress at fracture or rupture)
D. non of these
Q.13 ] Which testing machine is used for rebound
A. rock well hardness test .
B. knoop’s hardness.
C. Vicke’s hardness test
D. shoke’s scleroscope hardness
Q.14 ] The ease with which a given material can be removed or cut by cutting tools is known as ______.
A. Formability
B. Weldability
C. Machinability
D. Castability
Q.15 ] Ability of a material to resume original form on removal of load is called ________.
A. Strain
B. Elasticity
C. Elasticity
D. Malleability
Q.16 ] Cementite is iron carbide. It is hard and brittle. It possesses about _____% carbon.
A. 67%
B. 80%
C. 50%
D. None of above
Q.17 ] Ability of a materials to resists indentation, abrasion or scratching is called as _______.
A. Brittleness
B. Malleability
C. Hardness
D. Toughness
Q.18 ] That Heat- treatment process which is performed on steels mainly for refinement of their grain structure after hot or cold working is called as _______.
A. hardening
B. annealing
C. normalizing
D. non of these
Q.19 ] A surface hardening process for medium and high carbon steels making use of elastic induction heating principle is known as ______.
A. Flame Hardening
B. Case hardening
C. Nitriding
D. Induction Hardnening
Q.20 ] _______ is a supersaturated solution of carbon in α-iron formed by rapid cooling of austenite.
A. Austenite
B. Troostite
C. Martensite
D. Sorbite